Understanding ROE: A Key Metric for Investors

In the world of investing, understanding financial metrics is crucial for making informed decisions. One of these key metrics is Return on Equity (ROE). I aim to provide you with a clear and practical understanding of ROE, how to calculate it, and why it matters for your investment strategy.
What is ROE?
Return on Equity (ROE) is a financial ratio that measures a company’s ability to generate profits from its shareholders' equity. In simpler terms, it tells you how effectively a company is using the money invested by its shareholders to produce profits. ROE is expressed as a percentage and can give investors a snapshot of a company’s efficiency in generating returns.
How to Calculate ROE
The formula for calculating ROE is straightforward:

- Net Income: This is the company’s profit after all expenses, taxes, and interest have been deducted.
- Shareholders' Equity: This represents the net value of the company, which is the total assets minus total liabilities.
Example Calculation
Let’s break it down with an example. Suppose a company has a net income of $5 million and shareholders' equity of $25 million. Using the formula:
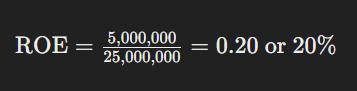
This means the company generates a 20% return on the equity invested by its shareholders, indicating a relatively efficient use of capital.
Why ROE Matters
ROE is particularly valuable for investors because it can indicate the quality of a company’s management and its ability to generate profits from its equity base. A higher ROE typically suggests that a company is effectively using its resources to create value for shareholders.
However, it’s essential to consider ROE in context. A high ROE might be due to high debt levels, which can increase financial risk. Conversely, a low ROE might not necessarily indicate poor performance; it could be a result of conservative financial management or a phase of significant capital investment for future growth.
ROE in Comparison
When analyzing ROE, it’s beneficial to compare it with:
- Industry Averages: Different industries have varying capital requirements and profitability norms. Comparing a company’s ROE with the industry average provides a benchmark for evaluation.
- Historical ROE: Reviewing a company’s ROE over several years can highlight trends and stability, showing whether the company consistently delivers good returns.
- Competitors: Comparing ROE with direct competitors helps assess how well a company performs relative to its peers.
Limitations of ROE
While ROE is a powerful tool, it’s not without limitations:
- Debt Influence: Companies can artificially inflate ROE by taking on more debt since the equity base becomes smaller relative to net income. This increases financial risk.
- Asset Write-Downs: Large write-downs can reduce equity and increase ROE, giving a misleading impression of performance.
- Non-Operational Factors: ROE doesn’t account for non-operational factors like market conditions or macroeconomic influences that can impact profitability.
Conclusion
ROE is a crucial metric for assessing a company’s profitability and efficiency in using shareholders' equity. However, it should not be the sole factor in your investment decisions. Always consider ROE alongside other financial metrics and qualitative factors to get a comprehensive view of a company’s performance and potential.
By understanding and applying ROE correctly, you can enhance your investment analysis and make more informed decisions. Happy investing!
